Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Millions of people worldwide suffer from widespread and frequent painful ailments known as carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Dr. Clement Yeh, a pain management physician, helps patients relieve pain associated with CTS. Numbness, tingling, and weakness of the hand and wrist were the defining symptoms. We will discuss the causes, signs, diagnosis, and available treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome in this educational article.
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
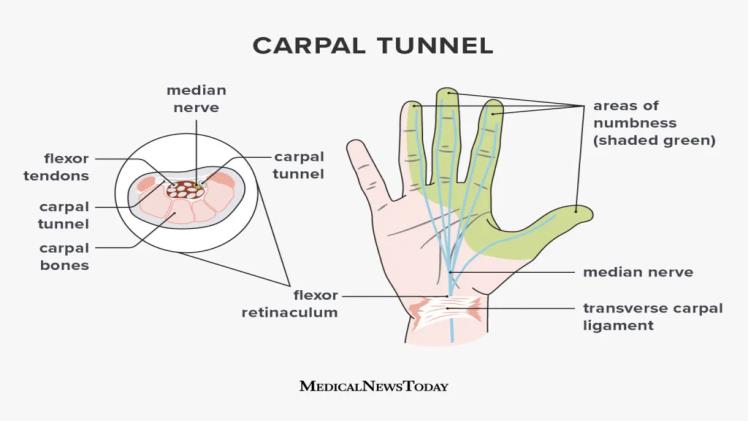
The wrist has a small opening called the carpal tunnel. It is made up of a ligament (the transverse carpal ligament) on the top and little wrist bones (carpal bones) on the bottom. The median nerve and many tendons involved in hand and finger movements pass through the tunnel.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Repeated hand and wrist motions: Typing for extended periods can cause the median nerve to become inflamed and compressed.
- Anatomical factors: The compression risk is increased in people who naturally have narrower carpal tunnels.
- Medical Conditions: Rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and hypothyroidism are a few conditions that can exacerbate CTS by producing swelling and fluid retention.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and fluid retention may stress the median nerve during pregnancy and cause transient CTS.
Common Symptoms of CTS
- Numbness and Tingling: The thumb, index, and middle fingers typically experience numbness and tingling as their first symptoms. These feelings frequently worsen at night.
- Weakness: People with CTS may suffer from hand weakness, which makes it challenging to grasp objects or perform fine motor tasks.
- Pain: Another typical sign of pain is pain in the wrist, hand, or forearm. The pain can radiate to the upper arm.
- Loss of Dexterity: Reduced hand dexterity can make tasks such as grasping utensils or buttoning clothes more difficult.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
A healthcare expert can identify CTS through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. To quantify nerve function and pinpoint the precise position and degree of compression, these tests may also involve electromyography and nerve conduction examinations.
Therapy Alternatives
- Conservative Measures: CTS can be treated conservatively in the early stages using rest, wrist splints, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapists can exercise to increase the strength and flexibility of the hands and wrists.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In circumstances, corticosteroid injections help reduce swelling and treat symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe or persistent cases, a surgical procedure called carpal tunnel release surgery may be advised. This surgery involves severing the transverse carpal ligament to relieve pressure on the median nerve.